
In this article, it will introduce the design of the SY8303 synchronous rectification Buck step-down chip circuit, including the schematic and PCB drawing processes, as well as the precautions and techniques.
Introduction of SY8303 Chip
SY8303 is a synchronous rectification Buck step-down chip, with TSOT23-8 package. The input voltage ranges from 4.5V to 40V, the maximum output current is 3A, the reference voltage is 0.6V, the output voltage is from 0.6V to 0.9Vin, and the switching frequency ranges from 500kHz to 2.5MHz.
Advantageous features: It offers low cost and high performance. It has low RDS(ON) for internal switches (top/bottom): 110/70 mΩ.
In this post it will use SY8303 to design a 24V to 12V, 2.5A, 500KHz DCDC converter. The design follows the guidance of https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1abUdYGEfv/. Thanks to Mr Tang.
Design Key Points
About the Frequency
The heating of DCDC chips is a critical issue. The heat consisted of the switching losses, conduction resistance losses, loss of magnetic components(inductor) and capacitor losses.
The conduction loss is regardless of the switching frequency is high or low, is equal. But when the switching frequency is high, the switching loss will increase.
The higher the switching frequency is the inductor value will be smaller. However, the switching loss will be greater, and the chip will generate more heat, the chip will become hotter.
Therefore, it is necessary to select the switching frequency carefully, and the inductor value should be selected to be a little smaller than the rated current.
So personally, suggest setting the switching frequency at 500KHz.
Capacitor selection
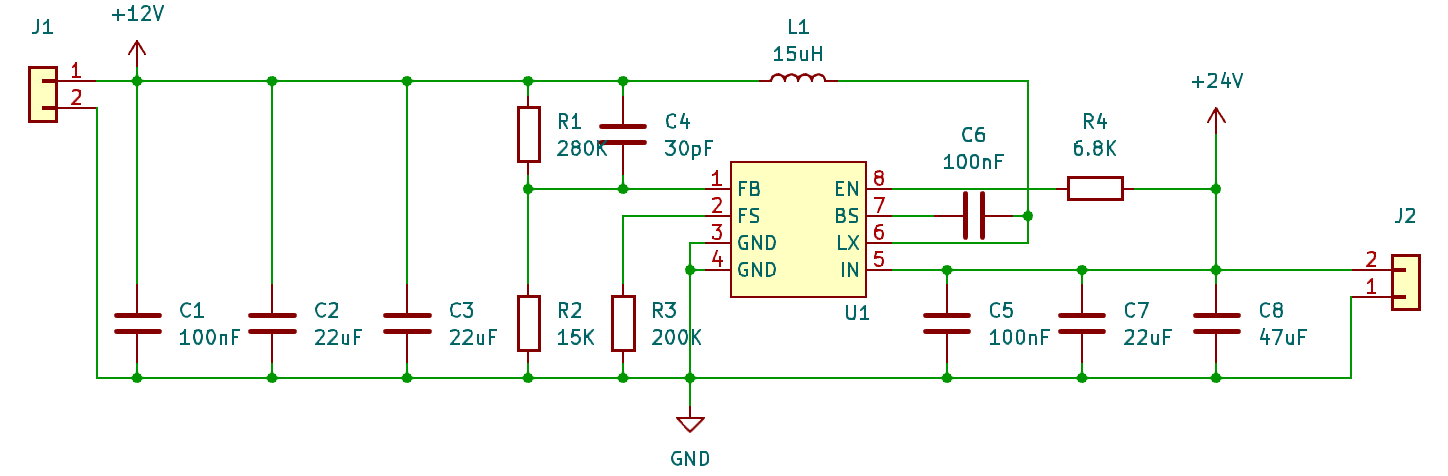
Input capacitor CIN: It is recommended to use a combination of large and small capacitances in parallel. The large capacitance has a voltage withstand of 35V and can be selected as 47μF, and the small capacitance is 0.1μF, placed close to the VIn and GND pins.
Output capacitor COUT: Also use a combination of large and small capacitances in parallel, with a voltage withstand of 25V. The capacity can be selected as 22μF, with the large capacitance close to the chip and the small capacitance beside the large one.
Bootstrap capacitor CBS: Has a value of 100nF and is placed close to the BS and LX pins.
Resistance settings
Feedback resistors R1 and R2: The value range is 10K - 1MΩ and are used to set the output voltage. For example, to output 12V, 15K and 280K resistors can be selected.
Switching frequency setting resistor RFS: The switching frequency equals to: Fsw = 10^5/RFS kHz, where RFS is in kΩ. If the switching frequency is set to 500KHz, RFS is 200KΩ.
Feedforward capacitor (optional): Can be paralleled on R3 and has a value as small as possible, such as 30pF.
The schematic shows as below figure:
Other key points
- Under-voltage protection: If under-voltage protection is not required, pins 1 and VR can be connected together or through a small resistor, but the resistor should not be too large.
- Switching frequency: A low switching frequency results in less heat generation for the chip, but a larger inductance is required; a high switching frequency requires a smaller inductance, but the chip has higher switching losses and significant heat generation.
- Inductor selection: The inductance value needs to be calculated based on the input and output voltages, current, and switching frequency. The rated current should be greater than or equal to 1.2 times the maximum IO. For example, when the input is 24V, the output is 12V, the current is 2.5A, and the switching frequency is 500KHz, an inductor of 15μH and a rated current of 4.5A can be selected.
Layout
-
Place capacitors, including CI (0.1μF and 47μF), CEO (25V 22μF), CBS (100 nF), etc. Pay attention to the capacitor package and voltage withstand value.
-
Place the inductor and select the appropriate inductance value and rated current based on the calculation.
-
Place resistors such as R1, R2, and RFS, and set the corresponding resistance values.
-
During layout, place CI close to the VI and GND pins, CBS close to the BS and LX pins, and the resistors connected to the FB close to the FB pin. The VO sampling point is after the last capacitor.
-
Perform special processing on the SW pin, such as expanding the copper area of the pin, opening windows, and tinning to aid in heat dissipation.
-
Add polygons on the top solder mask layer and expose copper for heat dissipation of the SW pin and inductor.
Wiring and copper plating
- Select an appropriate wire width for wiring, such as 8 mil or 10 mil, to ensure smooth traces.
- Switch to the bottom and top layers for copper plating, set the direct connection network rules with a spacing of 12 mil, and complete the copper plating.
- Place vias at positions such as CI and CEO, with an inner diameter of 12 mil, an outer diameter of 24 mil, and a row spacing of 40 mil to connect the top and bottom layers to assist in heat dissipation of the chip.
Precautions and Techniques
- Avoid common mistakes: Small values of CI and CO may lead to unstable output voltage and other issues.
- Improve technical content: For example, leave a gap at C7 to force the current through the filter capacitor.